how do leucine zippers work
Up to 10 cash back bZIP proteins are transcription factors that consist of three modular functional regions mediating dimerization DNA binding and transcriptional regulation. However many sequences have the leucine repeat but do not adopt the leucine zipper structure we shall refer to these as non-zippers.
The name arose because leucines occur every seven amino acids in this dimerization domain.
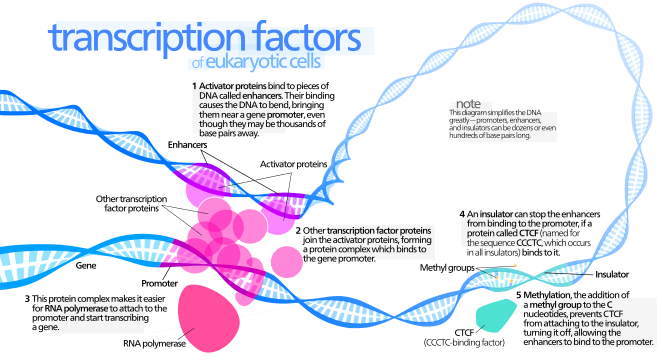
. When the protein is bound to the promotertranscription is stimulated and the gene is expressed. Leucine zippers contain a leucine in the d posi-tion of the repeating heptet 4 43 and can formwx homodimers eg as in GCN4 21 or het-wx erodimers eg as in Fos-Jun 21 51wx. The leucine zipper is a dimeric parallel coiled-coil but amphipathic helices can also oligomerize to form parallel coiled-coils that are trimers tetramers or pentamersThe majority of B-ZIP leucine zippers contain valines in the a positionandleucinesinthedpositionKimandcolleagues changed both of these amino acids to isoleucine which.
A zipper is closed when the hooks into those hollow areas. The zipper is made up of 2 main parts. If you look carefully at the teeth you will notice that each tooth is exactly the same distance away from the next and each one of.
On dimerization the leucine-zipper a helices form a parallel-coiled coil based on hydrophobic interfacial side-chain packing 55. L-leucine is the natural version of the amino acid is found in the proteins of the body and is the main form used as a supplement. These leucines are critical for the dimerization and DNA binding of B-ZIP proteins.
The leucine zipper is a protein-protein motif of -helices that dimerizes to form a coiled coil. At the COOH terminus an amino leucine occurs at every seventh position. How do helices dimerize in a leucine zipper.
Each one of the teeth has a hook and they are offset from one another so as they are pulled towards one another they connect in sequence. The hallmark of these proteins is the bZIP basic region leucine zipper domain a well-defined motif in eukaryotic proteins 1 2The basic region of the bZIP domain rich in lysines and arginines. The leucine zipper structure is adopted by one family of the coiled coil proteins.
Leu-XLeu-X-Leu-X-Leu where X may be any residue. Jakoby et al 2002. A slide which you use to open and close the zip and a set of teeth that are on either side the object you want to zip up.
Knobs into holes side chain packing. In this article well examine the various parts that make up a zipper and see how these components lock together so easily and securely. A More Stable Leucine Zipper.
The leucine zipper ZIP motif consists of a periodic repetition of a leucine residue at every seventh position heptad repeat and forms an α-helical conformation which facilitates dimerisation and in some cases higher oligomerisation of proteins by forming a parallel helixhelix association stabilised by formation of an interhelical hydrophobic core involving. The leucine zipper is an amphipathic a helix containing heptad repeats of Leu residues on one face of the helix and serves as a dimerization module. Despite the popularity of leucine among gym enthusiasts the science to back up most of its uses is weak.
Ranging in length from about 14 to 45 residues they are far shorter than other coiled coils 43wx. D-leucine is the mirror image of L-leucine which is created in the laboratory and is also used as a supplement. There have been a large number of experimental studies that.
Incorporation of unnatural amino acids into peptides and proteins modifies their properties in unique ways. Leucine Zipper with DNA1YSA- Leucine Zippers are a class of proteins that bind to DNA at specificsites within the promoters of genes. The zipper is so effective and reliable that in less than a hundred years it has become the de facto fastener for thousands of different products.
Long charged AAs via electrostatic interaction eg 4. Non-polar AAs via hydrophobicity ad 2. Third we have continued to work on the dimerization properties of mutant leucine zipper peptides.
The leucine zippers may be homo- or heterodimeric and thus increase their. Leucine zippers have a characteristic leucine repeat. A zipper has two rows of teeth on each side facing one another.
The leucine zipper is known to participate in DNA-binding and regulation of gene expression 45. The leucine zippers LZs represent particularly strong interaction domains commonly frequent in transcription factors2 and have been shown to be functional in a heterologous context3 4 5. A Form hydrogen bonds in the major groove of helices b Bind to one area of the DNA sequence c Start the formation complex d All of the above e None of the above Cells preserve their identity after cell division with which of the following.
In order for this to happen each of the teeth and hollows must be identical in size and shapeThe slide. Up to 10 cash back Dimeric regulatory proteins of two subunits. Secondly the C-terminus which is a leucine zipper region a heptad repeat of leucine or other bulky hydrophobic amino acids Ile Val Phe or Met creates an amphipathic helix.
The system is ingenious in its simplicity. Replacement of the normal C-terminal domain with a protein that can form oligomers will restore its DNA binding activity. What do leucine zippers do during transcription regulation.
The leucine zipper ZIP motif consists of a periodic repetition of a leucine residue at every seventh position and forms an α-helical conformation which facilitates dimerization and in some cases higher oligomerization of proteins. The leucine zipper is the dimerization domain of the B-ZIP basic-region leucine zipper class of eukaryotic transcription factors Vinson et al 1989. At the amino terminal domain positively charged amino acids are found and this region is bound to DNA in a zipper-like manner see Fig.
In many eukaryotic gene regulatory proteins the ZIP motif is flanked at its N -terminus by a basic region containing characteristic residues that. This class ofDNA binding proteins gets its name from the regular pattern of leucineresidues within the two alpha helices. New functionalities that do not exist in peptides containing only natural amino acids can be introduced which may be important in applications from drug design to enzyme catalysis.
Chargedpolar AAs via water mediated H bond ad 3. For the first part of the project we use the properties of bacteriophage lambda repressor. This region is involved in the dimerization of the bZIP protein before it binds to DNA Landschulz et al 1988.
The leucine zipper ZIP motif consists of a periodic repetition of a leucine residue at every seventh position and forms an a-helical conformation which facilitates dimerization and in somecaseshigheroligomerizationofproteins Inmanyeukaryoticgeneregulatoryproteins.

Chapter 13 Transcriptional Control And Epigenetics Chemistry

Dna Binding Motif An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
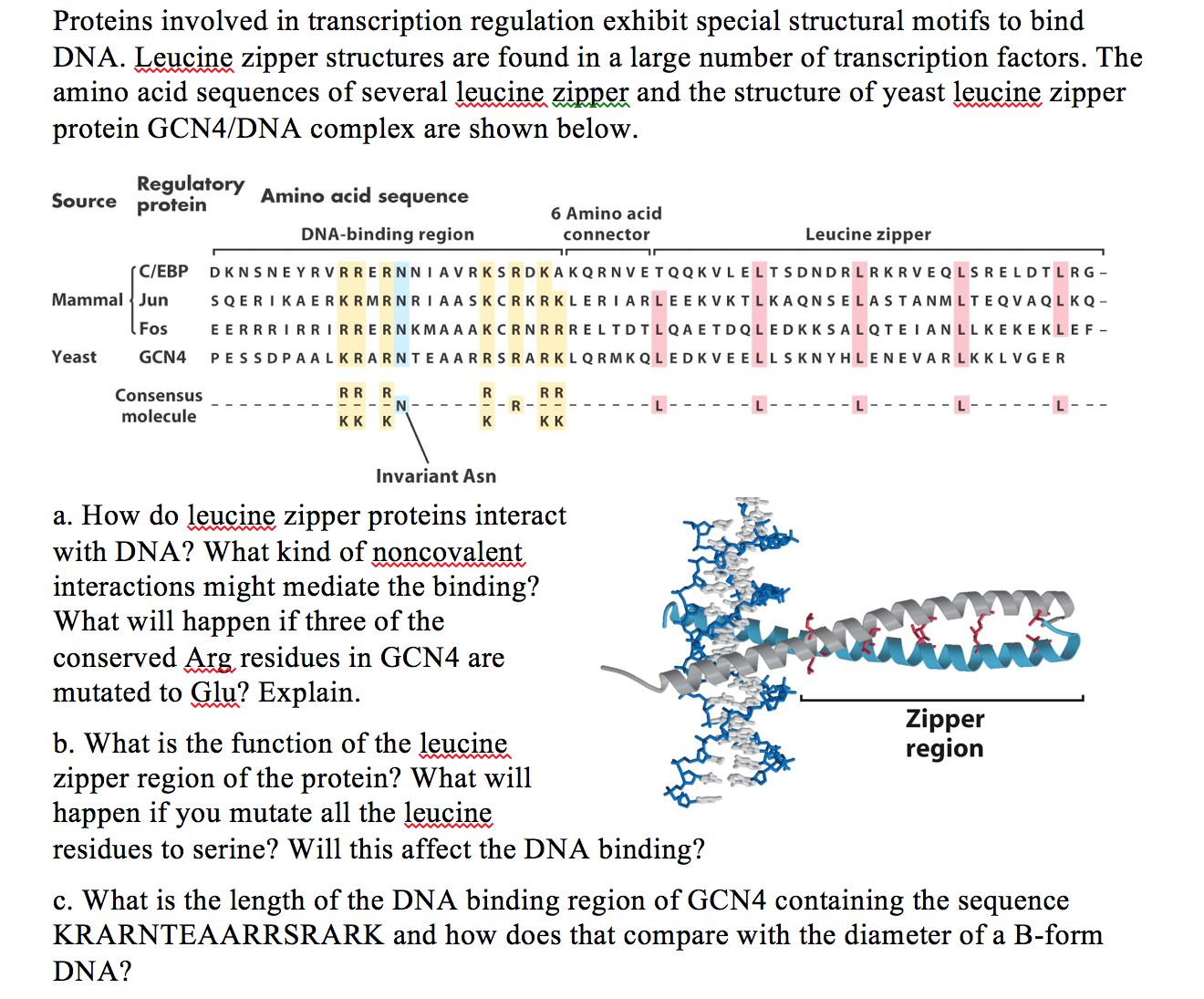
Solved Proteins Involved In Transcription Regulation Exhibit Chegg Com

9 Proteins Structure Function Relationship Flashcards Quizlet
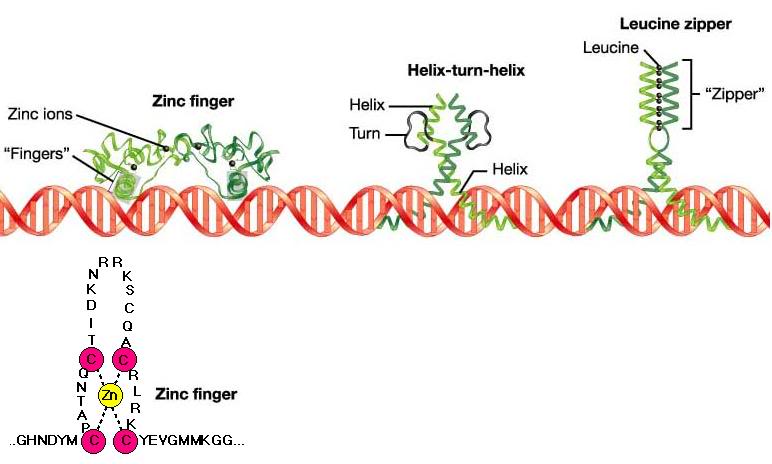
Transcription Factors Creative Diagnostics

Basic Leucine Zipper Transcription Factor An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Basic Leucine Zipper Transcription Factor An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Leucine Zipper Bearing Kinase Is A Critical Regulator Of Astrocyte Reactivity In The Adult Mammalian Cns Cell Reports

Transcription Central Dogma Genes Sequence Of Dna That

Alpha Helix An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Essential Amino Acids Chart Abbreviations And Structure Technology Networks

Transcription Factors Creative Diagnostics

A B Main Families Of Dna Binding Protein Domains The Proteins Are Download Scientific Diagram

Identification Of Activating Transcription Factor 4 Atf4 As An Nrf2 Interacting Protein Journal Of Biological Chemistry

A B Main Families Of Dna Binding Protein Domains The Proteins Are Download Scientific Diagram

